Call : 416 795 5000
ACE THE SAT for American Colleges
SAT Prep for American Colleges & Universities

What is the SAT?
The SAT is a standardized college admission test used by universities and colleges primarily in the United States, though it is also accepted by institutions in other countries. The SAT evaluates a student’s readiness for college by assessing skills in reading, writing, and math—key areas of academic achievement. Tutor STEM offers comprehensive SAT prep courses designed to help students strengthen their skills and perform well on each section of the exam. The SAT consists of three main sections: Evidence-Based Reading and Writing (which includes Reading Comprehension and Writing and Language), Math (divided into two parts: one allowing a calculator and one without), and an optional Essay section (which some colleges may require). The SAT serves as a critical component of the college admissions process, with most colleges using it as a tool to predict student success and to compare applicants from various educational backgrounds. Preparing for the SAT is essential, as it is often a key factor in admissions decisions and scholarship opportunities. The exam is known for its emphasis on critical thinking, problem-solving, and reasoning abilities, making it an important assessment for prospective college students.

What does the SAT consist of?
What sections are on the SAT and how long is the SAT?
The SAT consists of 3 main sections:
1) Evidence-Based Reading and Writing
- Reading (52 questions): This section tests your ability to read and interpret texts, analyze arguments, and understand the meaning of words in context. The reading passages cover a variety of topics including literature, history, social studies, and science.
- Writing and Language (44 questions): This section assesses your ability to revise and edit text, focusing on grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and logical flow. You'll be asked to improve sentences, identify errors, and make passages clearer and more concise.
2) Math
- No Calculator (20 questions): This part tests your ability to solve math problems without the use of a calculator. Topics include algebra, linear equations, and problem-solving with ratios, proportions, and percentages.
- Calculator (38 questions): This section covers more complex math topics, such as advanced algebra, functions, data analysis, and probability. A calculator is permitted for these questions, and you may use a scientific or graphing calculator.
3) Essay (Optional)
- Essay (1 prompt): The Essay section, which is optional, asks you to analyze a given argument and write a well-organized response that explains how the author builds their argument. You will be scored on reading, analysis, and writing skills.
If you are taking the Essay, there will be a total of 50 minutes added to the test duration, with no additional breaks specifically for the Essay section.
Is it possible to be granted more time on the SAT?
Applicants with documented disabilities or medical conditions may request accommodations for extended testing time or other necessary adjustments. The College Board, which administers the SAT, offers various accommodations based on individual needs, such as extended time, breaks, or alternate formats for test materials. Applicants must submit proper documentation and requests well in advance of the test date to be considered for accommodations.

What are the chances of getting into an Ivy League College or a Top Tier University?
Securing admission to an Ivy League school or other top-tier universities is an incredibly competitive process, as these institutions receive a high volume of applications from exceptionally talented students each year. While gaining acceptance is challenging, it is certainly achievable with the right preparation, experience, and strategy.
Ivy League schools, such as Harvard, Yale, Princeton, and Columbia, have low acceptance rates, often ranging from 4% to 8%. Top-tier universities, which include other prestigious institutions like Stanford, MIT, and the University of Chicago, also have similarly competitive admission processes with acceptance rates that typically fall between 6% and 15%. The low acceptance rates are due to the highly selective nature of these schools, which seek not only academically gifted students but also individuals with outstanding achievements in extracurricular activities, leadership, community involvement, and personal character.
In addition to stellar academic performance, many Ivy League and top-tier universities consider other factors such as SAT/ACT scores, personal essays, letters of recommendation, and interviews. These schools value applicants who demonstrate exceptional intellectual curiosity, a passion for learning, and the potential to contribute meaningfully to the campus community.
Admission to these schools often depends on strategic planning, beginning with early preparation for standardized tests like the SAT, participation in challenging courses (Advanced Placement or International Baccalaureate), and a demonstrated record of achievement beyond academics. Extracurricular activities such as volunteer work, internships, research, athletics, and leadership roles in clubs or organizations can significantly enhance an applicant's profile.
For instance, recent data suggests that students who worked with specialized SAT prep companies saw an average score increase of 150 points, which made a substantial difference in their chances of acceptance. With proper preparation and guidance, students can increase their likelihood of being accepted into an Ivy League or top-tier university by presenting a well-rounded, compelling application.
For several decades now, Tutor STEM has been helping students achieve outstanding SAT scores, significantly improving their chances of gaining acceptance into Ivy League colleges and other top-tier universities. Through personalized tutoring sessions and customized SAT prep strategies, Tutor STEM equips students with the skills, knowledge, and confidence needed to excel on the exam. Their experienced tutors work closely with students to identify strengths and areas for improvement, tailoring lessons to maximize performance in each section of the SAT. By providing comprehensive practice tests, test-taking strategies, and targeted feedback, Tutor STEM has consistently guided students to score in the top percentiles, making them competitive applicants for prestigious institutions. This dedication to student success has earned Tutor STEM a reputation for excellence, helping countless students secure their spots at highly selective universities.
Tutor STEM's SAT Tutoring Program

What preparation and tutoring does Tutor STEM provide for the SAT?
Tutor STEM offers comprehensive and individualized SAT tutoring designed to help students perform at their highest potential. The academy provides one-on-one tutoring sessions with carefully selected, highly qualified, and experienced instructors who are dedicated to guiding each student through the nuances of the SAT. Unlike group classes, Tutor STEM's personalized approach ensures that the instructor focuses entirely on the student's unique needs, maximizing learning outcomes and ensuring that no concept goes unaddressed. This tailored tutoring style is especially effective for students aiming to achieve top scores and secure spots at Ivy League and other prestigious universities.
Tutor STEM offers both in-person and virtual tutoring options, providing flexibility to students regardless of their location. In-person sessions can take place either at the academy’s facility or at the student’s home, with travel time and costs being factored into the price for home visits. Virtual tutoring, using an advanced online whiteboard software, ensures that students can benefit from the same level of interaction and personalized attention as they would in an in-person session. This online mode is ideal for students who are not within commuting distance but still seek top-tier SAT prep.
Included in the SAT preparation program are free study materials and resources that help reinforce the key concepts tested on the SAT. These resources, combined with the expert guidance of Tutor STEM’s instructors, are designed to equip students with the skills and strategies needed to excel in all sections of the SAT—Reading, Writing, and Math—ultimately enhancing their chances of acceptance to competitive universities.

How is the SAT Prep course structured?
1) Applicant registers for the SAT Preparation Course.
2) An assessment is held during the first tutoring session. The assessment is an accurate version of the most current version of the SAT. Based on the results of the initial assessment, an individualized plan that is tailored towards the applicant's strengths & weaknesses will be created by the Tutor STEM administration and the applicant's assigned SAT instructor based on the questions and concepts incorrectly answered on the assessment.
3) The majority of the materials, including the video lecture materials, practice tests, mock exams, and online resource drills will be distributed during the first class after the assessment is completed. The SAT instructor will devise a study plan with the student, after considering the students' other commitments (i.e. school or work), in order to ensure the self-studying that occurs outside of the 1-on-1 tutoring sessions the student has with the SAT instructor is spent efficiently.
4) The basis of the 1-on-1 tutoring sessions the student will have with the SAT instructor from the second tutoring session and onwards is based on the individualized plan, which is formulated using the data from the initial assessment the student completed during the first session. Essentially, the concepts the student was found to not understand or comprehend will be the focus of the 1-on-1 tutoring sessions.
5) The tutoring sessions will begin with the student asking the SAT instructor any questions they may have relative to the SAT, whether it be from the video lectures assigned to them or from any other resource. Typically, the first 15 minutes of every session is used to answer the students' pre-existing questions. Once the student has finished asking their questions, or if the student does not have any questions during the start of class, the SAT instructor will commence with the pre-planned lesson.
6) As the tutoring sessions come to a finish, the remaining materials and resources will be distributed to the student. The Blueprint, which is a free resource that is complimentary to the SAT Preparation course, is the last material/resource that will be distributed to the student. The Blueprint is a condensed study guide that organizes all of the concepts the student is expected to be tested on during their exam. The SAT instructor will thoroughly go over the Blueprint with the student, and will answer any questions the student may have pertaining to the concepts on the Blueprint.
7) The last tutoring session will consist of the student completing a diagnostic test, which is similar to the initial assessment the student will write during the first tutoring session. The diagnostic test is an accurate version of the most current version of the SAT. The student will complete the diagnostic. Based on the data of diagnostic results, the SAT instructor will be able to graphically and numerically show the student their improvement & progress throughout the SAT Preparation course. The SAT instructor will also give recommendations to the student on which concepts to prioritize self-studying based on the results of the final diagnostic.
8) During the final moments of the last tutoring session, the SAT instructor will devise a self-study plan with the student, for them to use and follow after the tutoring sessions have ended and before the date of their examination.

What resources & materials are included?
Resources and materials are included with the SAT Preparation Course for free. There is no additional cost for the resources and materials provided alongside the tutoring.
For students enrolling into the SAT Prep Program:
The resources and materials that are distributed to students prior to their SAT examination include:
- 1500 video lectures - 500 videos on calculator-based Math concepts, 500 videos on non-calculator-based Math concepts, 150 videos on Reading concepts, 150 videos on Writing & Language concepts, and 200 videos on Essay concepts.
- A collection of Practice Tests and Mock Exams that resembles similarly structured questions on the most recent versions of the SAT
- A collection of Multiple Drills and Question Sheets that resembles the same types of questions expected on the SAT
- Blueprint for the SAT - A concept sheet that is essentially a condensed study guide that organizes all of the concepts the student is expected to be tested on during their exam. The Blueprint is ordered from a third-party organization and is complimentary with the tutoring.
Math Concepts on the SAT Exam (Non-Calculator Section)
Algebra
Systems of Linear Equations
Systems of Linear Equations

Algebra in the No Calculator section of the SAT focuses on solving linear equations and inequalities, as well as systems of equations using methods like substitution and elimination. Students also simplify expressions by combining like terms and solve word problems by translating real-world situations into algebraic equations. Key skills include isolating variables, understanding properties of equality and inequality, and interpreting results in context. This section tests the ability to manipulate algebraic expressions and solve problems efficiently without the use of a calculator.
Systems of Linear Equations
Systems of Linear Equations
Systems of Linear Equations

Systems of linear equations involve two or more equations that share variables. The goal is to find a solution that satisfies all equations simultaneously. These systems can be solved through methods such as substitution, where you solve one equation for one variable and substitute it into the other, or elimination, where you add or subtract the equations to eliminate one of the variables. Understanding systems of linear equations is essential because they reflect real-world scenarios like finding the point of intersection of two lines, which is important in fields like economics, engineering, and physics.
Ratios and Proportions
Systems of Linear Equations
Ratios and Proportions

Ratios express the relative sizes of two quantities and are often written as a fraction, like a/b . A proportion is an equation that states two ratios are equal, such as a/b = c/d . These concepts are widely used in everyday life, such as determining the right amount of ingredients in recipes or scaling a model. A thorough understanding of ratios and proportions is vital for solving problems that involve scaling, comparing, or measuring quantities in various contexts.
Percents
Proportional Relationships
Ratios and Proportions

Percents represent parts of a whole and are often used to express changes in values. A percent can be written as a fraction out of 100, such as 20% being 2/100 or 0.20. Understanding percentages is essential for solving problems in finance (like finding tax or tip amounts), calculating discounts in shopping, or analyzing changes in quantities over time (such as increases in salary or price). The ability to work with percentages, including calculating percentage increase or decrease, is crucial for real-world applications.
Proportional Relationships
Proportional Relationships
Proportional Relationships

Proportional relationships describe situations where two quantities vary in a consistent way. A direct proportionality is often written as y=kx , where k is a constant. For example, if the number of workers doubles, the amount of work done might double as well. These relationships are fundamental in many fields such as economics, physics, and biology. Understanding how to identify, represent, and manipulate proportional relationships allows you to solve a variety of practical problems, like calculating speed, distance, and time in motion problems or understanding financial calculations.
Word Problems
Proportional Relationships
Proportional Relationships

Word problems require you to translate a narrative into a mathematical equation or inequality. These problems often involve real-life situations, such as planning a budget, determining distances or times, or working with mixtures or proportions. Solving word problems typically involves identifying the key variables, determining the relationship between them, and then applying the appropriate mathematical concepts, such as solving for an unknown in an equation or inequality. The skill of interpreting and solving word problems is essential because it connects mathematical concepts to practical situations.
Exponents
Coordinate Geometry
Exponents

Exponents represent repeated multiplication. For example, x^3 means (x)(x)(x). Exponent rules, such as the product of powers rule (x^a)(x^b)=(x^(a+b)), are used to simplify expressions and solve equations. Working with exponents is also important in understanding scientific notation, which is commonly used to express very large or small numbers, like the size of atoms or the distance between planets. Mastery of exponents enables you to handle complex expressions and solve problems in algebra, physics, and other fields.
Radicals
Coordinate Geometry
Exponents

Radicals involve roots, such as square roots or cube roots. The square root of a number is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3×3=9. Radicals are used in many areas, including geometry (to find distances or angles in right triangles), algebra (to solve equations), and even in real-world scenarios like calculating dimensions of physical objects. Simplifying radical expressions and solving equations involving square roots or cube roots is crucial in problem-solving.
Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate Geometry
Quadratic Equations & Expressions

Coordinate geometry deals with geometric shapes and their properties using the coordinate plane. The coordinate plane is made up of two perpendicular number lines, typically called the x-axis and y-axis. Points are located based on their x and y coordinates. Coordinate geometry involves solving problems that relate to slopes of lines, distance between points, midpoint of a line segment, and equations of lines. These concepts are vital for understanding graphs, analyzing geometric shapes, and solving real-world problems like navigation, design, and construction.
Quadratic Equations & Expressions
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning
Quadratic Equations & Expressions

Quadratic equations involve variables raised to the second power (squared), like (x^2)−(5x)+6=0 . These equations can often be solved by factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Quadratic equations are used in various practical applications, such as determining the trajectory of a projectile or solving optimization problems in economics. Understanding how to solve quadratic equations is critical for success in higher mathematics and many real-world situations.
Linear Equations and Inequalities
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning

Linear equations involve expressions that form a straight line when graphed. These equations typically have variables raised to the first power, such as y = 2x + 3. Solving these equations means finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true. Inequalities are similar, but instead of an equals sign, they involve greater than, less than, or equal to symbols. Solving inequalities means determining a range of values for the variable that satisfies the inequality. Understanding how to manipulate these equations and inequalities is crucial because these problems form the basis for much of algebra and problem-solving.
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning
Problem-Solving & Quantitative Reasoning

Problem-solving and quantitative reasoning in the No Calculator section of the SAT involves applying mathematical concepts to real-world situations. It focuses on interpreting data, analyzing relationships between quantities, and solving word problems using logic and algebra. Students must reason through problems involving ratios, percentages, and proportions, and apply mathematical principles to solve them without a calculator. This section tests the ability to make decisions based on quantitative information and solve problems efficiently.
Math Concepts on the SAT Exam (Calculator Section)
Linear and Quadratic Functions
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods

Linear functions represent relationships where the rate of change between the variables is constant. They are expressed in the form y=mx+b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Quadratic functions, on the other hand, represent relationships where the rate of change is not constant and involve squared variables. These are written in the form y=ax^2+bx+c. Both types of functions are essential in modeling real-world situations such as growth, movement, and optimization.
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods

Solving systems of equations involves finding values for variables that satisfy multiple equations simultaneously. These systems can involve linear or non-linear equations, and methods to solve them may include substitution, elimination, or graphing. Advanced methods may also involve using matrices or other tools to find solutions to systems of equations. These systems often arise in business, economics, and other fields where multiple factors interact simultaneously.
Rational Expressions and Equations
Systems of Equations with Advanced Methods
Rational Expressions and Equations

Rational expressions are fractions where the numerator and/or denominator is a polynomial. Rational equations involve expressions like these, and solving them requires finding values for the variable that do not make the denominator zero. These types of problems are important for understanding proportions, rates, and real-world phenomena such as speed, efficiency, and production rates. Mastery of rational expressions helps in simplifying complex algebraic fractions and solving real-world problems.
Probability and Statistics
Probability and Statistics
Rational Expressions and Equations

Probability is the study of likelihood and involves understanding how likely events are to occur. It’s often calculated by comparing the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes. Statistics involves collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. Topics include measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), measures of spread (range, standard deviation), and analyzing distributions. These concepts are critical for making informed decisions based on data and are used extensively in fields like business, social sciences, and health.
Complex Numbers
Probability and Statistics
Complex Numbers

Complex numbers consist of a real part and an imaginary part, typically written in the form a+bi, where i is the imaginary unit and i^2=−1. Operations with complex numbers include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Complex numbers are used in many fields such as engineering and physics to solve problems that involve quantities with both real and imaginary components, such as electrical circuits or wave phenomena.
Trigonometry
Probability and Statistics
Complex Numbers

Trigonometry is the study of relationships between the angles and sides of triangles, particularly right triangles. The main trigonometric functions include sine, cosine, and tangent, which relate the angles of a triangle to the ratios of its sides. Trigonometry is used in various applications such as physics (for analyzing waves, sound, and light), engineering (for designing structures and systems), and navigation (for determining positions and routes).
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms

Exponents represent repeated multiplication, and advanced exponent rules involve working with expressions that include powers of powers or multiplying/dividing terms with exponents. Logarithms are the inverse of exponents and are used to solve equations where the variable is an exponent, such as 2^x=8. Logarithms are used in fields like computer science (for algorithms and data structures), finance (for calculating compound interest), and science (for measuring exponential growth or decay).
Functions and Their Inverses
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms
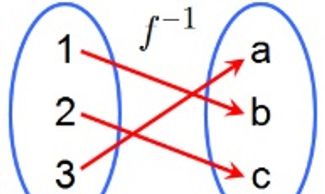
Functions are mathematical relationships where each input (usually x) corresponds to exactly one output (usually y). Inverses of functions reverse this relationship. For example, the inverse of f(x)=2x+3 is f^−1(x)=(x−3)/(2). Functions and their inverses are important in algebra, calculus, and applied mathematics. Understanding how to work with functions and their inverses helps solve problems in a variety of scientific and engineering disciplines.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
Advanced Exponent Rules and Logarithms
Data Interpretation and Analysis

This concept involves analyzing data presented in various forms such as graphs, charts, or tables. Data interpretation helps in understanding trends, making predictions, and analyzing relationships between variables. This skill is crucial for interpreting research findings, making business decisions, and drawing conclusions based on evidence. Understanding how to analyze and interpret data allows you to make informed decisions in fields like science, economics, and public policy.
Polynomial Expressions
Experimental interpretation
Data Interpretation and Analysis

Polynomials are algebraic expressions made up of terms that are added or subtracted, with variables raised to whole-number powers. Operations with polynomials include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Understanding how to manipulate polynomials is important for solving higher-level algebraic equations and understanding more complex mathematical relationships. Polynomials are often used in fields like engineering, physics, and economics to model complex systems and phenomena.
Experimental interpretation
Experimental interpretation
Experimental interpretation

Experimental interpretation in the Math section of the SAT involves analyzing data from experiments or real-world scenarios. This may include interpreting tables, graphs, or charts that represent statistical or experimental data. Students are asked to extract meaningful information, identify trends, and make inferences or predictions based on the data presented. It tests the ability to understand and interpret quantitative information, such as averages, distributions, and relationships between variables, to draw conclusions or solve problems. This skill is essential for working with data in fields like science, economics, and social studies.
Scatterplots and graphs
Experimental interpretation
Experimental interpretation

Scatterplots and graphs in the Calculator section of the SAT involve analyzing data points plotted on a coordinate plane. Scatterplots show the relationship between two variables by displaying individual data points, and students must interpret trends, patterns, or correlations in the data. This can include identifying whether the relationship is linear or nonlinear, recognizing outliers, and determining the strength of the correlation. Additionally, students may be asked to interpret information from other types of graphs, such as bar graphs, line graphs, or histograms, to draw conclusions or make predictions based on the visual data representation. Understanding how to analyze and interpret these graphs is key to solving problems in various fields, including science, economics, and social studies.
Reading Concepts on the SAT Exam
Main Idea and Central Theme
Main Idea and Central Theme
Main Idea and Central Theme

The main idea refers to the overarching point or argument of a passage, while the central theme represents the deeper message, especially in literary or historical passages. SAT Reading questions often ask students to summarize the passage’s core argument or determine what the author is primarily discussing. This skill is critical for comprehending long, complex texts quickly, helping test-takers avoid getting lost in details.
Supporting Evidence
Main Idea and Central Theme
Main Idea and Central Theme

Supporting evidence questions require students to locate textual proof for their answers. These questions often follow main idea or inference-based questions and ask students to select a line or paragraph that supports their response. This skill is essential because it ensures that students can ground their interpretations in actual text, an ability crucial for academic reading and critical thinking.
Inference and Implication
Main Idea and Central Theme
Inference and Implication

Inference questions test a student’s ability to read between the lines and determine unstated ideas based on textual clues. These questions are significant because they assess a reader's capacity to synthesize information, a skill necessary for both college and real-world problem-solving. The SAT frequently disguises these questions with wording like “The passage most strongly suggests that…”
Author’s Purpose and Tone
Passage Structure and Organization
Inference and Implication

These questions evaluate why an author wrote a passage and their attitude toward the subject. Common purposes include persuading, informing, or entertaining, while tone can range from neutral to passionate or sarcastic. Recognizing these elements is vital because it helps students grasp the author’s intent and approach, preventing misinterpretation.
Word in Context
Passage Structure and Organization
Passage Structure and Organization

Instead of testing vocabulary in isolation, the SAT assesses how words function within specific contexts. These questions often ask for synonyms of words used in the passage, but the correct answer must align with the passage's meaning. This skill is important because words can have multiple definitions, and understanding them in context is crucial for both academic and everyday reading.
Passage Structure and Organization
Passage Structure and Organization
Passage Structure and Organization

These questions focus on how an author organizes their argument or information. Students may be asked about paragraph function, transitions, or the effectiveness of a specific sentence. Recognizing structure helps students understand complex arguments and follow the logical flow of information, a necessary skill for effective reading and writing.
Dual Passages Analysis
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)

Some SAT Reading sections contain two shorter, related passages. These questions ask students to compare viewpoints, analyze similarities and differences, or determine how one passage might respond to the other. This skill is critical for evaluating multiple perspectives, which is essential in academic discussions and real-world debates.
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)

The SAT Reading section includes scientific and historical passages that contain charts, graphs, or tables. Students must interpret data, understand its relationship to the text, and answer questions based on it. This is significant because it tests students' ability to analyze quantitative information, an essential skill for STEM and social science fields.
Function of a Sentence or Paragraph
Data Interpretation (Graphs & Tables)
Function of a Sentence or Paragraph

These questions ask why an author includes a specific sentence or paragraph and how it contributes to the overall argument. Students must determine whether a statement provides evidence, introduces a new idea, or serves another purpose. This skill is important because recognizing textual functions improves comprehension and writing clarity.
Argument and Rhetorical Strategies
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis
Function of a Sentence or Paragraph

These questions evaluate how an author builds and supports their argument. Students may need to identify rhetorical techniques such as appeals to logic, emotion, or credibility. This is a crucial skill for understanding persuasive writing and preparing for college-level essay writing.
Historical and Literary Contexts
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis

Certain SAT passages come from historical speeches or classic literature. These questions assess a student’s ability to understand outdated language, references, and the broader historical or literary significance. This skill is essential for interpreting complex texts encountered in higher education.
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis
Difficult Sentence and Syntax Analysis

Some SAT Reading questions focus on particularly dense or complex sentences. Students must untangle lengthy, clause-filled sentences to determine meaning. This skill is crucial for handling college-level reading, where texts often contain intricate sentence structures.
Writing Concepts on the SAT Exam
Sentence Structure & Boundaries
Sentence Structure & Boundaries
Sentence Structure & Boundaries

These questions test knowledge of complete vs. incomplete sentences, run-ons, and proper sentence separation using punctuation. This skill is crucial for writing clarity and coherence, preventing common grammatical errors.
Verb Tense, Mood, and Voice
Sentence Structure & Boundaries
Sentence Structure & Boundaries

Students must ensure correct verb tense consistency, understand subjunctive mood, and distinguish between active and passive voice. These rules are important because errors in tense and voice can make writing unclear and grammatically incorrect.
Pronoun Usage and Agreement
Sentence Structure & Boundaries
Pronoun Usage and Agreement

These questions assess proper pronoun-antecedent agreement and clarity in pronoun reference. Proper pronoun use is essential for avoiding ambiguity and ensuring grammatical correctness in both formal and informal writing.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Modifier Placement and Clarity
Pronoun Usage and Agreement

This concept ensures that singular subjects take singular verbs and plural subjects take plural verbs, even in complex sentence structures. Mastery of this rule is crucial for sentence clarity and grammatical correctness.
Modifier Placement and Clarity
Modifier Placement and Clarity
Modifier Placement and Clarity

Misplaced or dangling modifiers create confusion by attaching descriptions to the wrong nouns. The SAT tests a student’s ability to place modifiers correctly to maintain logical sentence meaning.
Parallel Structure
Modifier Placement and Clarity
Modifier Placement and Clarity

Parallel structure ensures consistency in lists, comparisons, and paired ideas. SAT questions often ask students to revise sentences to maintain grammatical symmetry, improving readability and formal writing effectiveness.
Punctuation Rules
Conciseness and Redundancy
Word Choice and Precision

The SAT Writing section frequently tests comma usage, semicolons, colons, dashes, and apostrophes. Proper punctuation is necessary for writing clarity and sentence fluidity, making it an essential skill for academic and professional writing.
Word Choice and Precision
Conciseness and Redundancy
Word Choice and Precision

These questions test a student’s ability to select the most precise word to convey a sentence’s meaning. Strong word choice is essential for effective communication, ensuring that writing is clear, professional, and impactful.
Conciseness and Redundancy
Conciseness and Redundancy
Conciseness and Redundancy

This concept involves analyzing data presented in various forms such as graphs, charts, or tables. Data interpretation helps in understanding trends, making predictions, and analyzing relationships between variables. This skill is crucial for interpreting research findings, making business decisions, and drawing conclusions based on evidence. Understanding how to analyze and interpret data allows you to make informed decisions in fields like science, economics, and public policy.
Logical Transitions
Sentence and Paragraph Order
Conciseness and Redundancy

Polynomials are algebraic expressions made up of terms that are added or subtracted, with variables raised to whole-number powers. Operations with polynomials include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Understanding how to manipulate polynomials is important for solving higher-level algebraic equations and understanding more complex mathematical relationships. Polynomials are often used in fields like engineering, physics, and economics to model complex systems and phenomena.
Sentence and Paragraph Order
Sentence and Paragraph Order
Sentence and Paragraph Order

Experimental interpretation in the Math section of the SAT involves analyzing data from experiments or real-world scenarios. This may include interpreting tables, graphs, or charts that represent statistical or experimental data. Students are asked to extract meaningful information, identify trends, and make inferences or predictions based on the data presented. It tests the ability to understand and interpret quantitative information, such as averages, distributions, and relationships between variables, to draw conclusions or solve problems. This skill is essential for working with data in fields like science, economics, and social studies.
Tone, Style, and Formality
Sentence and Paragraph Order
Sentence and Paragraph Order

Scatterplots and graphs in the Calculator section of the SAT involve analyzing data points plotted on a coordinate plane. Scatterplots show the relationship between two variables by displaying individual data points, and students must interpret trends, patterns, or correlations in the data. This can include identifying whether the relationship is linear or nonlinear, recognizing outliers, and determining the strength of the correlation. Additionally, students may be asked to interpret information from other types of graphs, such as bar graphs, line graphs, or histograms, to draw conclusions or make predictions based on the visual data representation. Understanding how to analyze and interpret these graphs is key to solving problems in various fields, including science, economics, and social studies.
Contact Us
#1 SAT Prep Course
Tutor STEM has been helping individuals from all sorts of academic backgrounds & career portfolios score high percentile scores on the SAT through personalized tutoring and updated SAT prep materials, in order to facilitate college acceptance in the United States.
Tutor STEM's SAT preparation program is available for students in Canada and in the United States.
Tutor STEM SAT Department
30 New Delhi Drive, Markham, Ontario L3S 0B5, Canada
Call: 416 795 5000 Email: admin@tutorstem.ca Markham Campus Scarborough Campus Downtown Toronto Campus
SAT Department Office Hours
Mon | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Tue | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Wed | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Thu | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Fri | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Sat | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. | |
Sun | 06:00 a.m. – 11:30 p.m. |
Ontario Education Group